
Theoretical vs Experimental Probability YouTube
Experimental probability | Statistics and probability | 7th grade | Khan Academy Calculus 2 Lecture 7.1: Integration By Parts It's cable reimagined No DVR space limits. No long-term contract..

Theoretical vs. Experimental Probability Anchor Chart Poster Anchor charts, Theoretical
The chance of a happening is named as the probability of the event happening. It tells us how likely an occasion is going to happen; it doesn't tell us what's happening. There is a fair chance of it happening (happening/not happening). They'll be written as decimals or fractions. The probability of occurrence A is below.

Experimental vs Theoretical Probability Theoretical vs Experimental Probability
See What Users Love About Opera Desktop. Download the Browser today. Don't miss Opera Browser: The ultimate browsing experience.
Unit 6 Probability
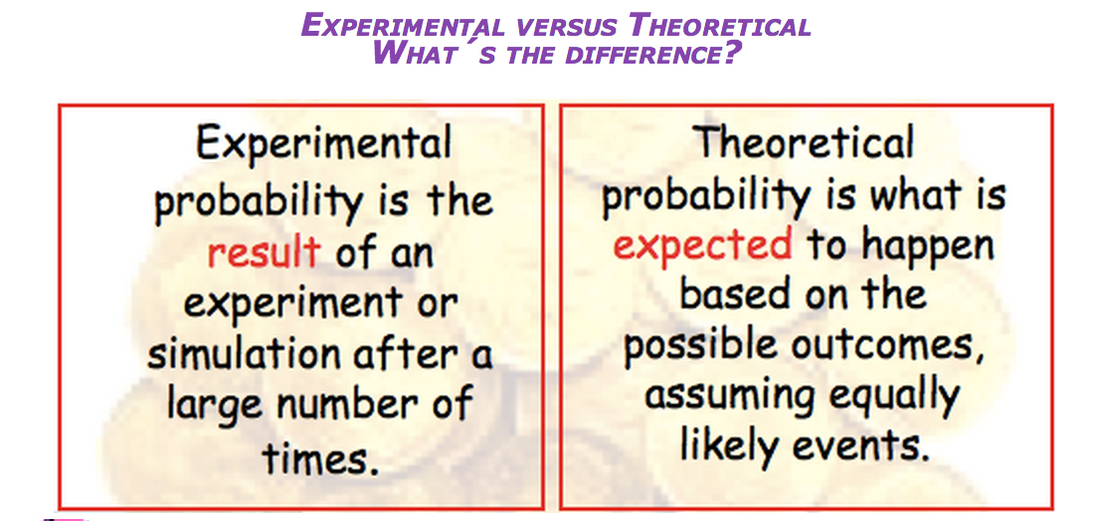
In order words, theoretical probability represents how likely an event is to happen. On the other hand, experimental probability illustrates how frequently an event occurs in an experiment. Read on to find out the differences between theoretical and experimental probability.

PPT Experimental vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID9333065
138 Share 16K views 2 years ago This video teaches viewers about experimental probability and theoretical probability. The video includes an example of experimental probability and.

PPT Experimental Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID1379596
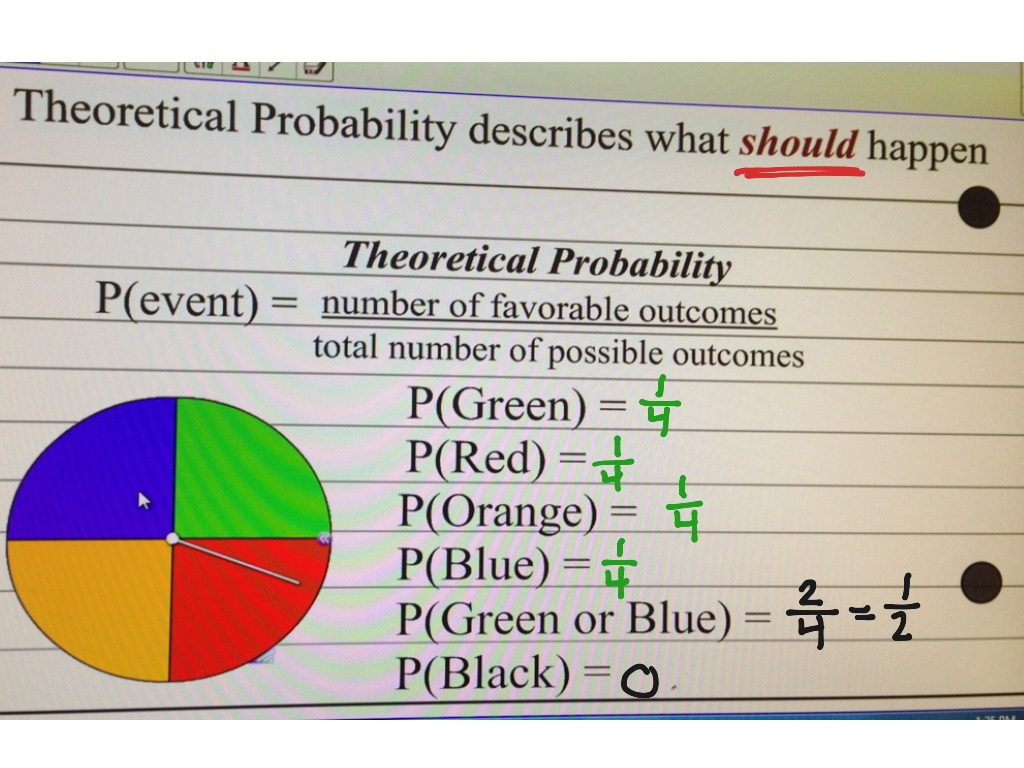
1. Use the table below to determine the probability of each number on a number cube. Let's Review: Theoretical probability is what we expect to happen, where experimental probability is what actually happens when we try it out.

PPT Experimental Probability Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID6032335
#Probability #Matheducation #Instructabeats #mathGuided Notes: https://docs.google.com/document/d/1SqmCSbrV2oYZhbamcm9blZuVdYvo8MLt23Rg1yRWR_g/copy

Theoretical vs. Experimental Probability YouTube
Probability is the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of outcomes. In this case that would be the number of simulations with 3 or more flips divided by the total number of simulations. Well, there weren't any simulations with 3 flips, there was one simulation with 4 flips. and one simulation with 5 flips.

Seventh grade Lesson Theoretical vs Experimental Probabilities
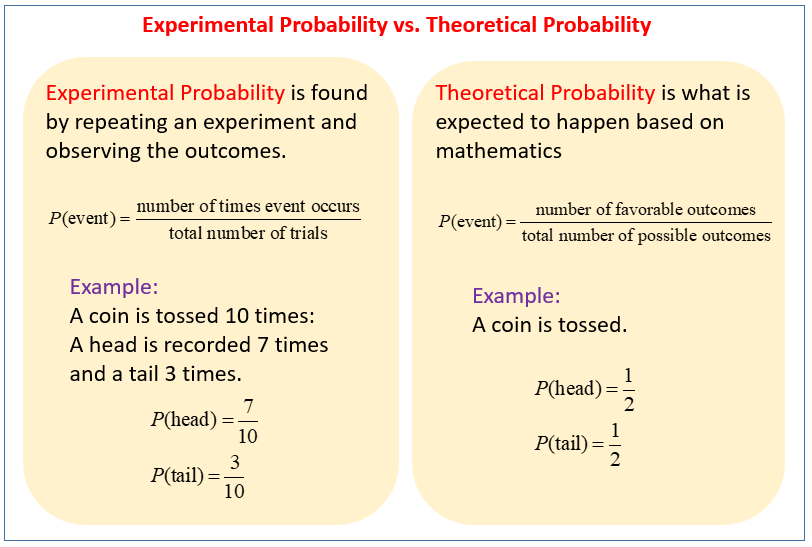
The experimental (or empirical) probability of an event is an " estimate " that an event will occur based upon how often the event occurred after collecting data from an experiment in a large number of trials. This type of probability is based upon direct observations. Each observation in an experiment is called a trial. Example:

PPT Experimental Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID1379596
Transform Your Marks Into Grade-A Achievements With Osmosis's Unique Study Tools. Osmosis helps train your brain with resources designed to lock in key info for good.
Experimental and Theoretical Probability Math ShowMe
Blake S 6 years ago Experimental probability is the results of an experiment, let's say for the sake of an example marbles in a bag. Experimental probability would be drawing marbles out of the bag and recording the results. Theoretical probability is calculating the probability of it happening, not actually going out and experimenting.

Experimental vs Theoretical Probability Theoretical vs Experimental Probability
Figure 4-4 shows a graph of experimental probabilities as n gets larger and larger. The dashed yellow line is the theoretical probability of rolling a four of 1/6 \(\neq\) 0.1667. Note the x-axis is in a log scale. Note that the more times you roll the die, the closer the experimental probability gets to the theoretical probability. Figure 4-4

PPT 11.2 Theoretical and Experimental Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID2537712
Theoretical probability describes how likely an event is to occur. We know that a coin is equally likely to land heads or tails, so the theoretical probability of getting heads is 1/2. Experimental probability describes how frequently an event actually occurred in an experiment.

PPT Experimental Probability Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID9487309
Experimental Probability In this video, we are going to learn about the differences between theoretical and experimental probability. After you finish this lesson, view all of our Algebra 1 lessons and practice problems. Let's use rolling a dice as an example. Use P to represent probability.
Theoretical Probability and Experimental Probability (solutions, examples, games, videos)
A Results from an experiment don't always match the theoretical results, but they should be close after a large number of trials. Dave's coin is obviously unfair. B Dave's coin is obviously unfair. question d Dave continues flipping his coin until he has 100 total flips, and the coin shows heads on 47 of those flips.

PPT Experimental Probability Vs. Theoretical Probability PowerPoint Presentation ID1300985
Experimental probability is the ratio of the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials. In other words, theoretical probability is a ratio that describes what should happen, but experimental probability is a ratio that describes what actually happened. You can use theoretical and experimental probabilities to distinguish.